Giovanni Bolcato 1 Maicol Bissaro 1. Protease inhibitors interfere with HIVs ability to make new viruses inside the CD4 cells.
- The virus contains reverse transcriptase RT an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase which makes a DNA copy of the viral RNA - This DNA copy is integrated into the genome of the host cell and it is then termed a provirus - The provirus DNA is transcribed into both new genomic RNA and mRNA for translation into viral proteins using host cell machinery.
Viral protease inhibitors mechanism of action. Action mechanism of antiviral drugs consists of its transformation to triphosphate following the viral DNA synthesis inhibition. The current paradigm for HCV treatment relies on pegylated interferon and ribavirin as agents that enhance endogenous mechanisms for viral clearance and are dependent on host factors. It inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteases.
HIV-1 protease and blocking proteolytic cleavage of protein precursors that are necessary for the production of infectious viral particles. Protease breaks down HIV proteins using those. An analysis of the action mechanism of known antiviral drugs concluded that they can increase the cells resistance to a virus interferons suppress the virus adsorption in the cell or its diffusion into the cell and its deproteinisation process in the cell amantadine along with antimetabolites that causes the inhibition of nucleic acids synthesis.
This is in accordance with the presumed mode of action of lopinavir and ritonavir as viral protease inhibitors which is supposed to inhibit virus replication by interfering viral polypeptide processing. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors are active against HIV a retrovirus. Protease breaks down HIV proteins using those smaller particles to make new viruses that can mature and spread.
The nucleostide reverse transcriptase inhibitors NRTIs are activated by phosphorylation in two steps. A different two-step mechanism has been suggested Li 2016 and in this case the virion binds to a receptor on the target host cell surface through its S1 subunit and the Spike is cleaved by host proteases Hasan et al 2020 and then it is expected the fusion at low pH between viral and host target membranes via S2 subunit. Protease inhibitors interfere with HIVs ability to make new viruses inside the CD4 cells.
However this hypothesis needs further experimental evidence. Computational insights into the mechanism of action of the protease inhibitors lopinavir ritonavir and nelfinavir. Treatment of one may affect outcome of the other in co-infected individuals.
An analysis of the action mechanism of known antiviral drugs concluded that they can increase the cells resistance to a virus interferons suppress the virus adsorption in the cell or its. Protease inhibitors prevent viral replication by selectively binding to viral proteases eg. In patients with genotype 1 HCV infection sustained viral response SVR rates remain suboptimal with less than half of genotype 1-infected individuals going on to achieve SVR.
An analysis of the action mechanism of known antiviral drugs concluded that they can increase the cells resistance to a virus interferons suppress the virus adsorption in the cell or its diffusion into the cell and its deproteinisation process in the cell amantadine along with antimetabolites that causes the inhibition of nucleic acids synthesis. Mechanism of action. HIV protease is an aspartate protease which splits viral protein molecules into smaller fragments and it is vital to both the replication of the virus within the cell and also to.
Drugs that inhibit the VIRAL PROTEASE that is required at the late stage of the replicative cycle to cleave the viral gag and gag-pol polypepetide precursors to form the mature. Mechanism of action Nelfinavir is a protease inhibitor. Specifically they block an enzyme known as protease.
The drugs inhibit RNA virus replication by reversible inhibition of viral HIV reverse transcriptase which reverse transcribes viral RNA into DNA for insertion into the host DNA sequence see Fig. We show these protease inhibitors augment the antimalarial activity of artemisinin against P. HIV protease inhibitors indinavir or nelfinavir are important antiretroviral drugs and artemisinin is central to malaria treatment.
Specifically they block an enzyme known as protease. HIV protease systematically cleaves individual proteins from the gag and gag - pol polypeptide precursors into functional subunits for viral capsid formation during or. Infection and HIV.
Targeting the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Finally the viral genetic material a single stranded RNA is fully released. Protease inhibitors target viral proteases which are key enzymes for the completion of viral maturation.

Pdf Hiv Protease Inhibitors A Review Of Molecular Selectivity And Toxicity
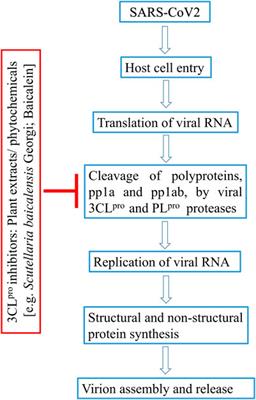
Frontiers Plant Products As Inhibitors Of Coronavirus 3cl Protease Pharmacology

Vorinostat Saha Bar Chart Class

Checkpoint Inhibitors Creative Peptides Checkpoint Inhibitors Peptide Synthesis Peptides

A Hiv 1 Infection Pathway And B Antiretroviral Drug Arv Action Download Scientific Diagram

Mechanism Of Action Hiv 1 Protease Inhibitor Download Scientific Diagram

Nsc23005 Sodium Sodium Stem Cells Novels

Hiv Mechanisms Of Action Of Protease Inhibitors Pis Youtube
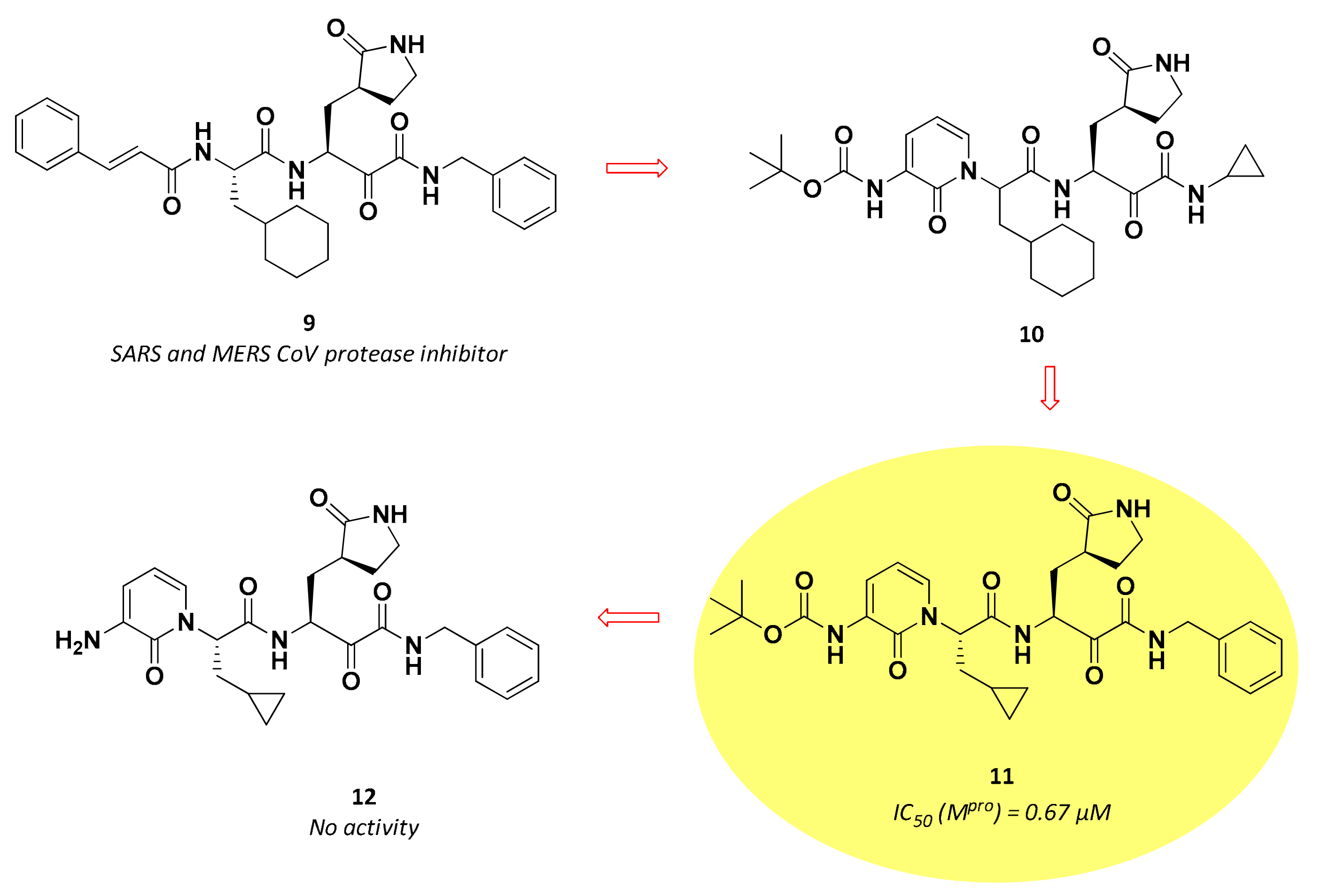
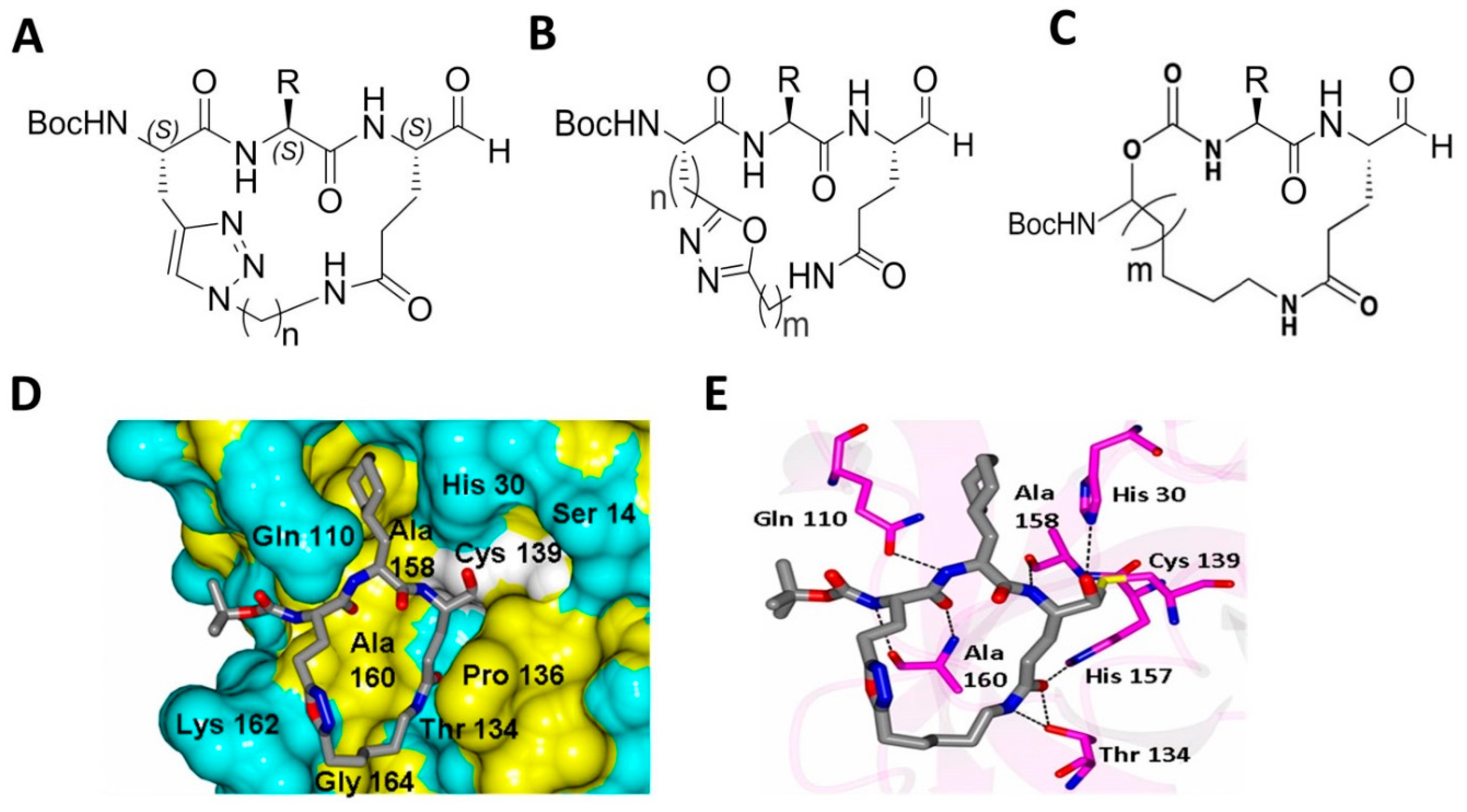
Biomolecules Free Full Text Sars Cov 2 Mpro A Potential Target For Peptidomimetics And Small Molecule Inhibitors Html
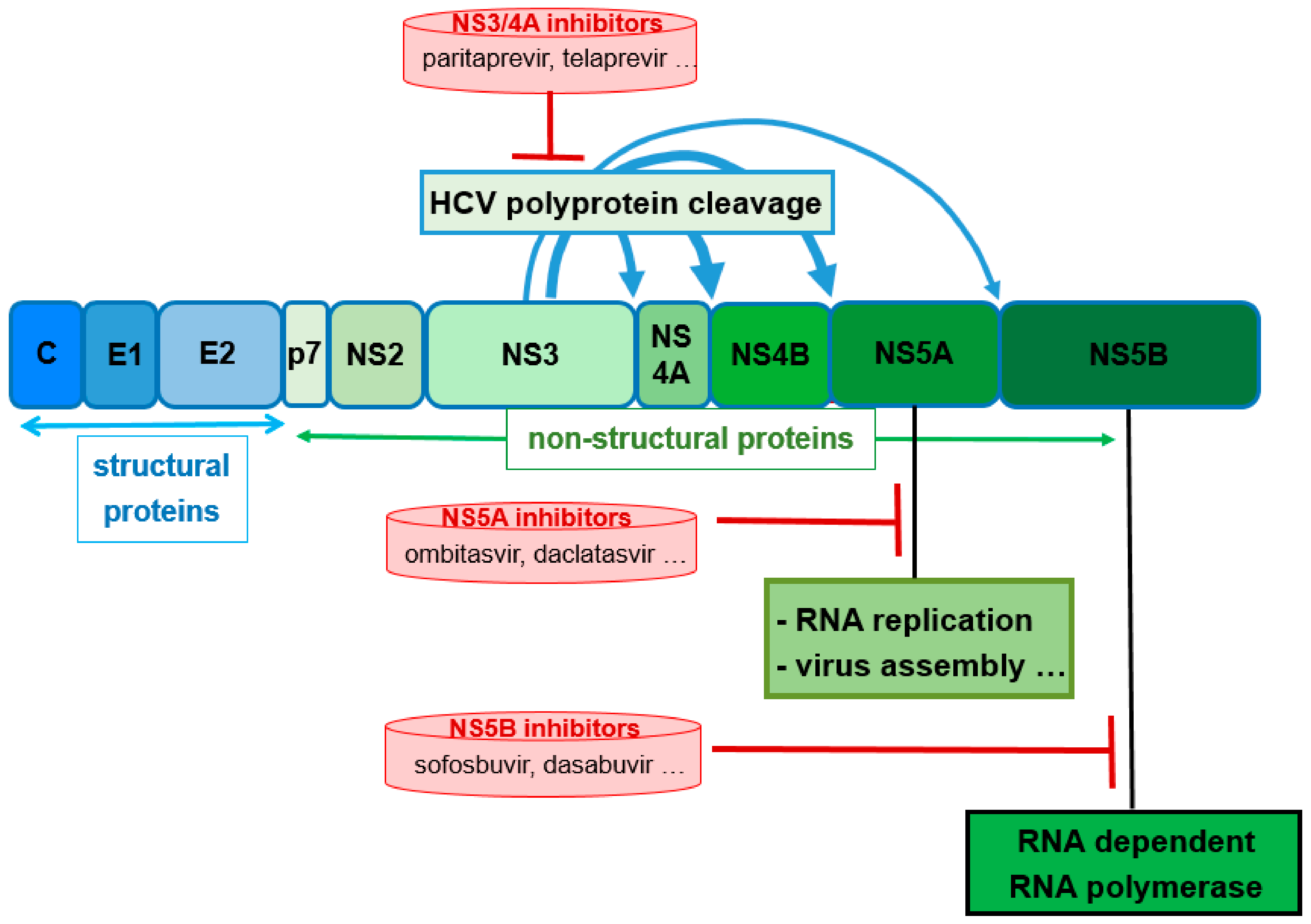
Sci Pharm Free Full Text Pharmacokinetic Enhancers Boosters Escort For Drugs Against Degrading Enzymes And Beyond Html

Viruses Free Full Text Antiviral Drug Discovery Norovirus Proteases And Development Of Inhibitors Html
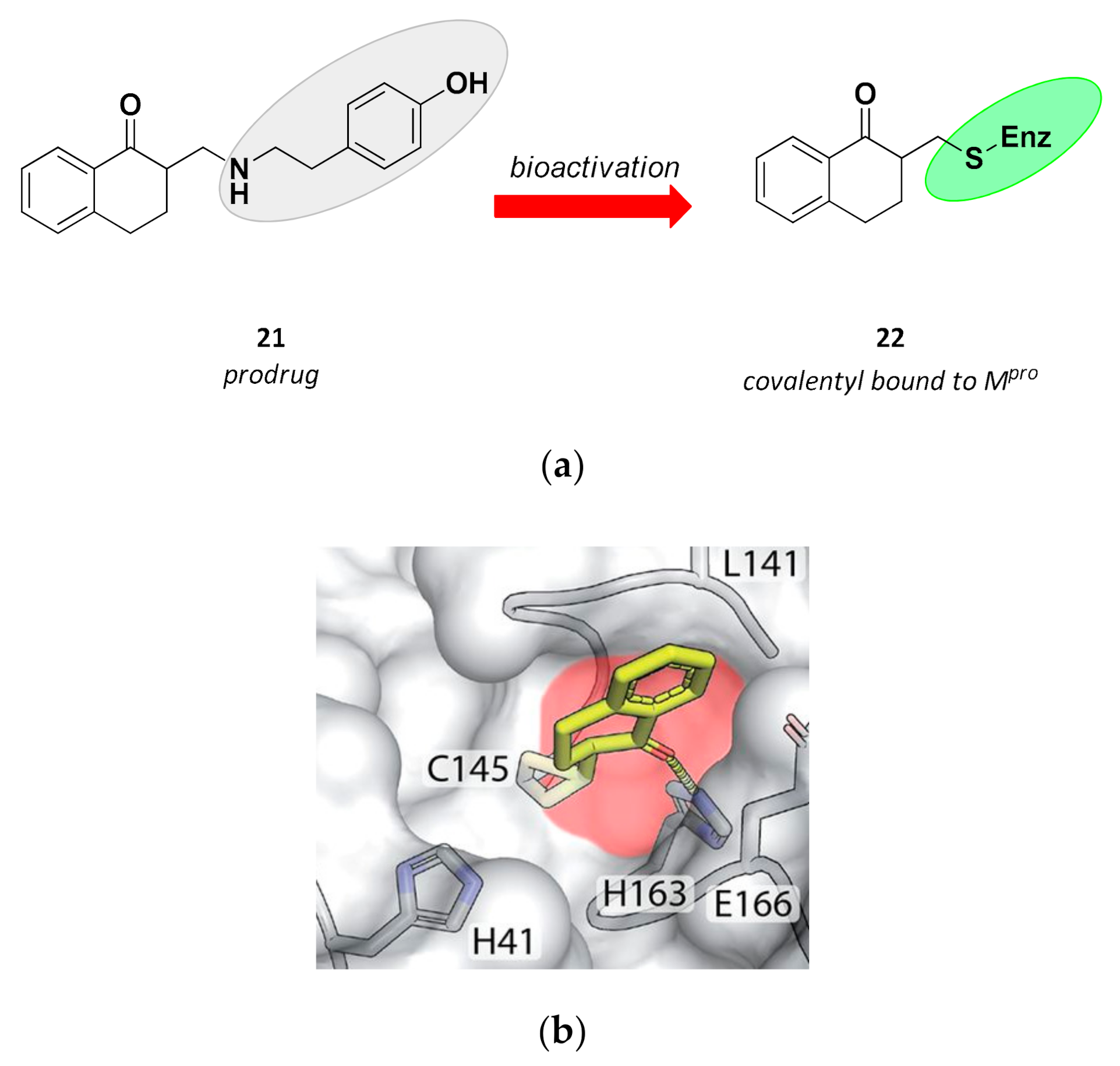
Biomolecules Free Full Text Sars Cov 2 Mpro A Potential Target For Peptidomimetics And Small Molecule Inhibitors Html

2s Octyl A Hydroxyglutarate Home Decor Decals Decor







